Fact sheet
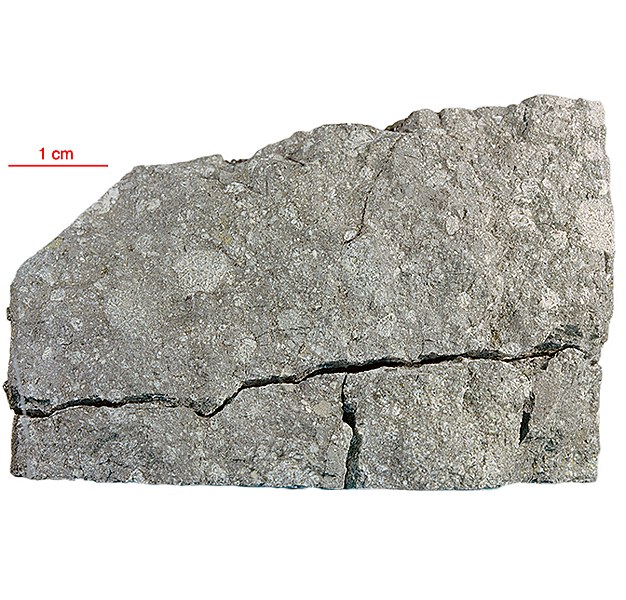
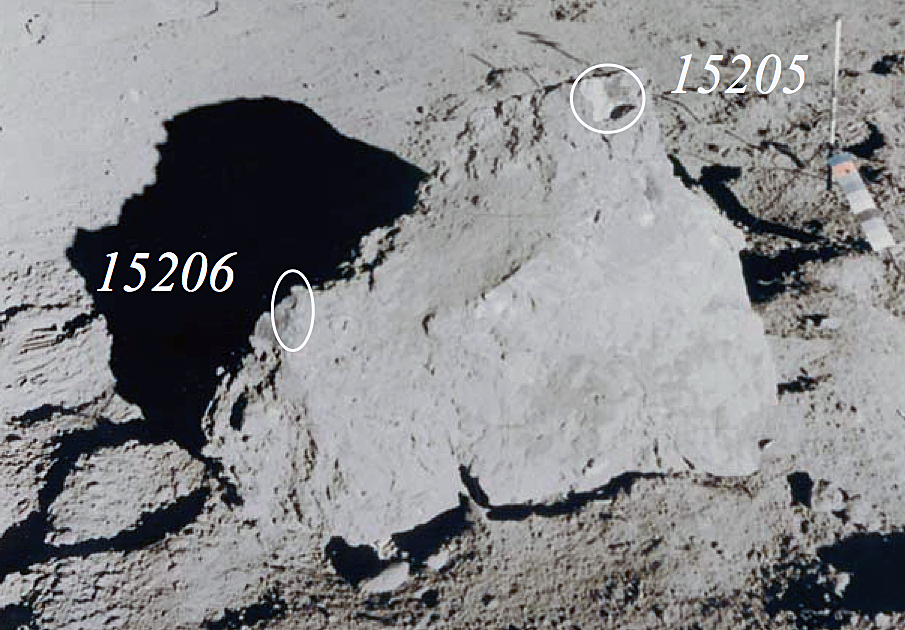
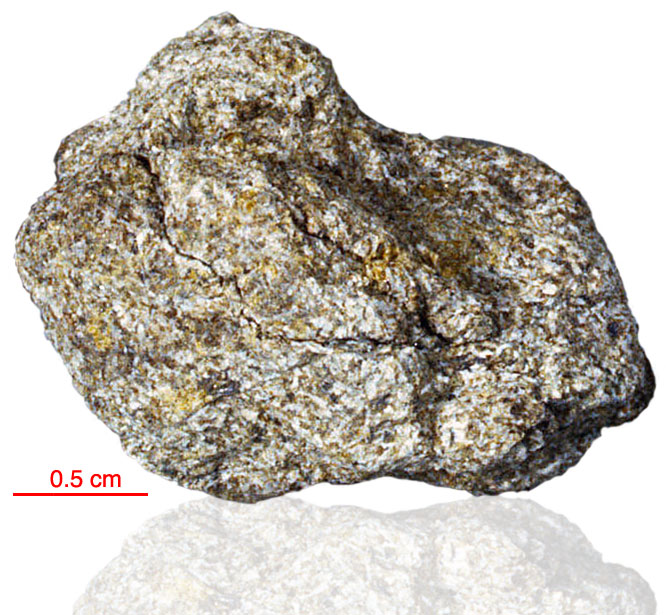
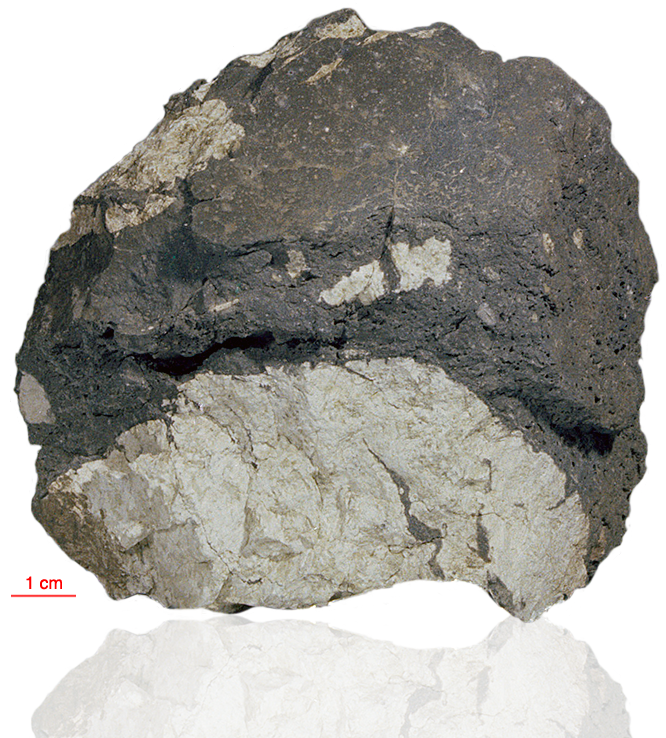
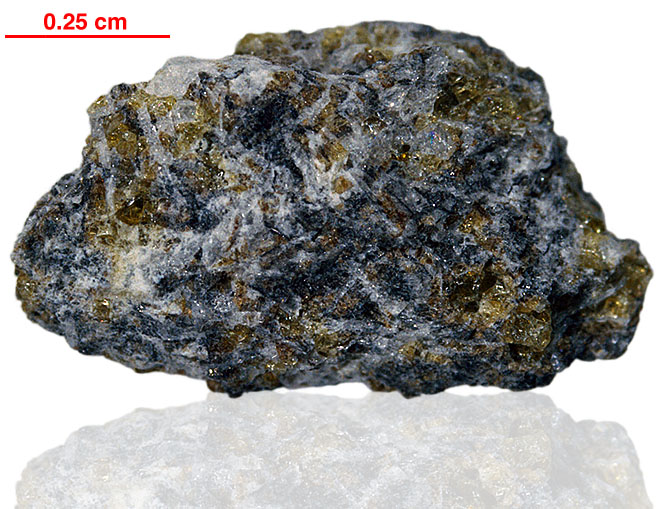
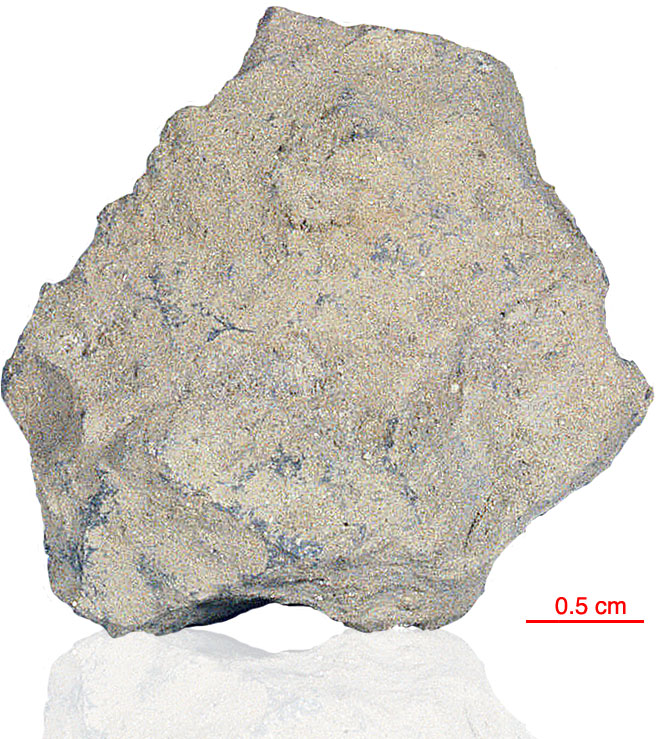
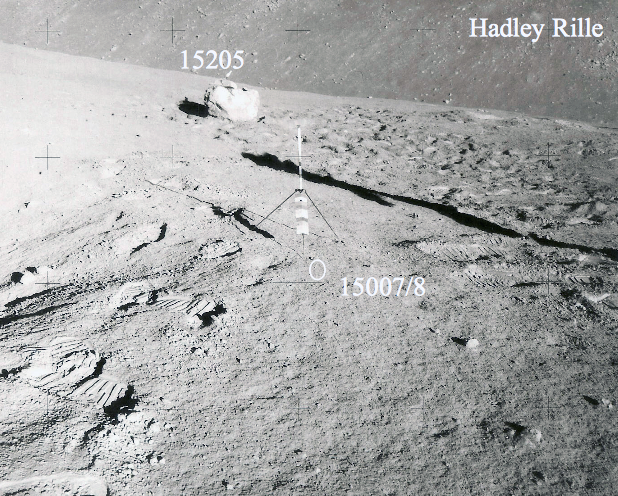
15205 is noteworthy in that it contains a high percentage of KREEP basalt fragments as clasts, but also contains fragments of the mafic green glass, and mare basalt found in the Apollo 15 regolith. Brown KREEP glass is also present. 15205 is clast rich and matrix poor with little evidence of clast-matrix interaction. There is a pronounced fabric. The thin glass coating on five out of six sides of 15205 is unusual (see rotation 2).
The sample weighed 337.3 grams before analysis. A zircon from this sample has been dated at 4.01±0.11 billion years (Pb/Pb).
Further details of this and other Apollo samples are here: http://curator.jsc.nasa.gov/lunar/
KREEP is an acronym built from the letters K (the atomic symbol for potassium), REE (Rare Earth Elements) and P (for phosphorus). It is a geochemical component of some lunar impact breccia and basaltic rocks.
The Apollo 15 landing site was in the Apennine Highlands, and close to Hadley Rille — a long, narrow winding valley. Approximately 76 kg of lunar material, including soil, rock, core-tube and deep-core samples, were returned to Earth.
This mission was the first flight of the Lunar Roving Vehicle which allowed the astronauts to venture further from the Lunar Module than in previous missions. During three periods of extravehicular activity, or EVA, on July 31st, and August 1st and 2nd, Scott and Irwin completed a record 18 hours, 37 minutes of exploration, travelling 17.5 miles, in the first car that humans had ever driven on the Moon.
Apollo 15 was launched on 26 July 1971.